Migraine
Headache
Migraine is a type of headache that occurs as an attack and causes severe or pounding pain. The headache develops suddenly. Sometimes even in the middle of the night. The pain is usually located on one side of the head.
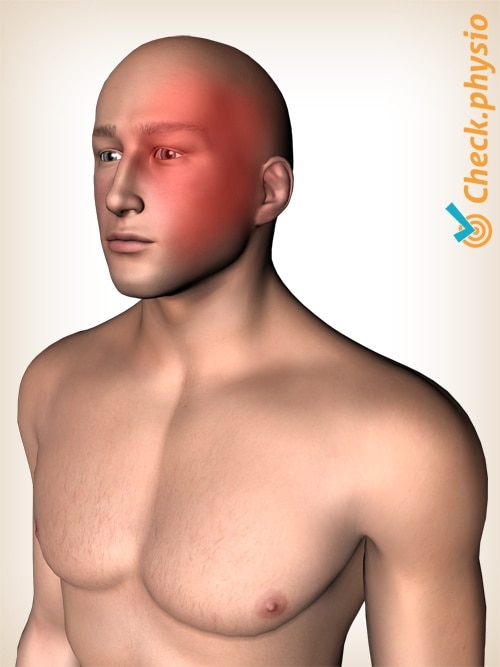
Other forms of headache include tension headache, medication-induced headache, cluster headache and cervicogenic headache.
Description of the condition
A distinction is made between migraine with aura and migraine without aura. An aura means that the patient exhibits neurological symptoms, such as seeing flashes of light, spots or blotches. The patient can also suffer loss of vision, pins and needles, loss of strength and speech disruption. Migraine without aura is the most common.
Cause and origin
The exact cause of migraine is not known.
Signs & symptoms
The patient has suffered at least five attacks of headache, lasting 4 - 72 hours. In addition, a number of the following symptoms can occur:
- The pain is throbbing or pounding, and moderate to severe.
- Exertion makes the symptoms worse.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- The patient tries to avoid lights and sounds.
If the patient suffers migraine with aura, the patient can experience flashes of light, spots or blotches in the field of vision. Sometimes the patient suffers vision problems or speech disruption. Pins and needles or decreased sensitivity of the skin are also possible. The aura symptoms last no longer than an hour and precede the headache.
Diagnosis
Treatment
This condition is usually treated with medication. Analgesics can reduce the severity of the attacks. A single dose of ibuprofen, paracetamol or aspirin reduces the pain in many cases.
Exercises
You can check your symptoms using the online physiotherapy check or make an appointment with a physiotherapy practice in your area.
References
Nugteren, K. van & Winkel, D. (2012). Onderzoek en behandeling van de nek. Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum.


